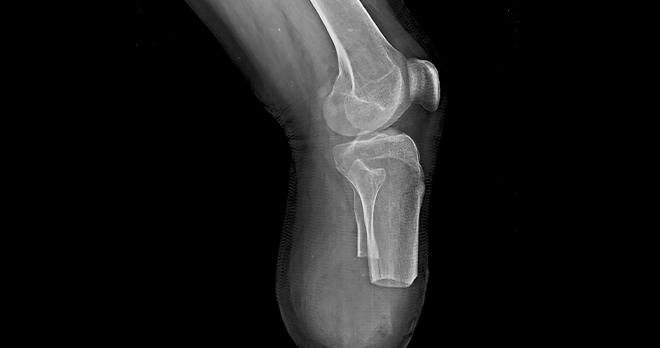
Compartment syndrome – what you need to know, and when injury is due to negligence
Compartment syndrome is a painful and potentially serious condition caused by bleeding or swelling within an enclosed bundle of muscles, a muscle compartment, usually in the arms and legs. It occurs when pressure within a compartment builds, restricting the blood flow to the area, and can cause serious damage to the muscles and nerves.
Types of compartment syndrome
- Acute – this happens suddenly, usually after a fracture or crush injury often of the arm or leg. It is a medical emergency and requires urgent treatment, ideally within a few hours.
- Chronic – this happens gradually, usually during and immediately after repetitive exercise like running or cycling, and passes within a few minutes of stopping the activity.
This blog will focus on acute compartment syndrome, which can be a cause of amputation. If missed by medical professionals the consequences can therefore be life-changing.
Signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome
Symptoms usually develop after an injury and quickly get worse.
Symptoms can include:
- intense pain, especially when the muscle is stretched (much worse that would be expected for the severity of the injury)
- swelling, tenderness or tightness in the muscle
- a tingling or burning sensation and in severe cases, numbness or weakness (which are signs of permanent damage)
Beyond a physical examination, definite diagnosis requires a direct measurement of the pressure by inserting a needle into the compartment and recording the pressure using a pressure monitor.
What are the causes of compartment syndrome?
Causes include:
- a broken bone or crush injury (the most common cause)
- a plaster cast or tight bandage being applied to a limb before it has stopped swelling
- burns (which can cause the skin to become scarred and tight)
- surgery to repair a damaged or blocked blood vessel
How do you treat compartment syndrome?
Acute compartment syndrome is a medical emergency and requires immediate surgery to reduce the pressure and avoid permanent damage to the muscles or nerves.
The surgical procedure used is called a fasciotomy: a surgeon makes long incisions through the skin and fascia layer underneath to relieve excessive pressure. The wound is usually closed a few days later, but occasionally a skin graft may be required to cover the wound.
When can compartment syndrome lead to amputation?
Left untreated, compartment syndrome can lead to severe tissue or nerve damage, muscle loss and the release of harmful toxins which can cause kidney failure.
Severe infection, especially where the muscle is not receiving adequate blood flow, can make amputation a necessary and life-saving procedure.
At RWK Goodman, we support people who have been affected by a delay in recognising and treating compartment syndrome leading to amputation. We help them navigate the legal process in obtaining compensation for potentially avoidable limb loss and limb difference.
As you can tell from the above, there are clear signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome and if they are missed due to a lack of reasonable care on the part of a medical professional, the consequences are very severe and ultimately life-changing. If this is the case, you may have a claim for compensation as a result of amputation.
Our aim is to raise awareness of this condition so that people are better informed about the signs and symptoms, and there is a greater awareness of the risks associated with compartment syndrome.
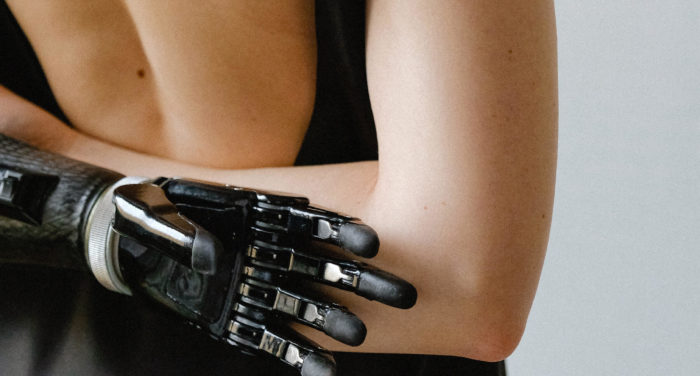
Read our guide to amputations
If you have experienced limb loss, find out more about choosing the right prosthetic, the support available to you, and more in our guide.
Our guide covers what you need to know about types of amputation, rehabilitation, prosthetics, support networks and more.
If you have suffered limb loss as a result of negligent treatment of compartment syndrome, and want to find out whether you can make a claim for compensation, please contact our team today.
Call now
Read more on limb loss
Read more about amputation from our Info Hub
View more articles related to Amputation